PFAS in Drinking Water: The Hidden Danger and How Reverse Osmosis Can Protect Your Health
Share
PFAS in Drinking Water: The Hidden Danger and How Reverse Osmosis Can Protect Your Health
PFAS, or “forever chemicals,” have made their way into drinking water across the country, sparking health concerns that range from hormone disruption to cancer. Found in everyday products like non-stick cookware and waterproof clothing, PFAS chemicals are notoriously difficult to remove from the environment—and from our water supply. In this post, we’ll explore why PFAS are so dangerous and how reverse osmosis (RO) systems are one of the most effective solutions for eliminating them from your water.
What Are PFAS and Why Are They So Dangerous?
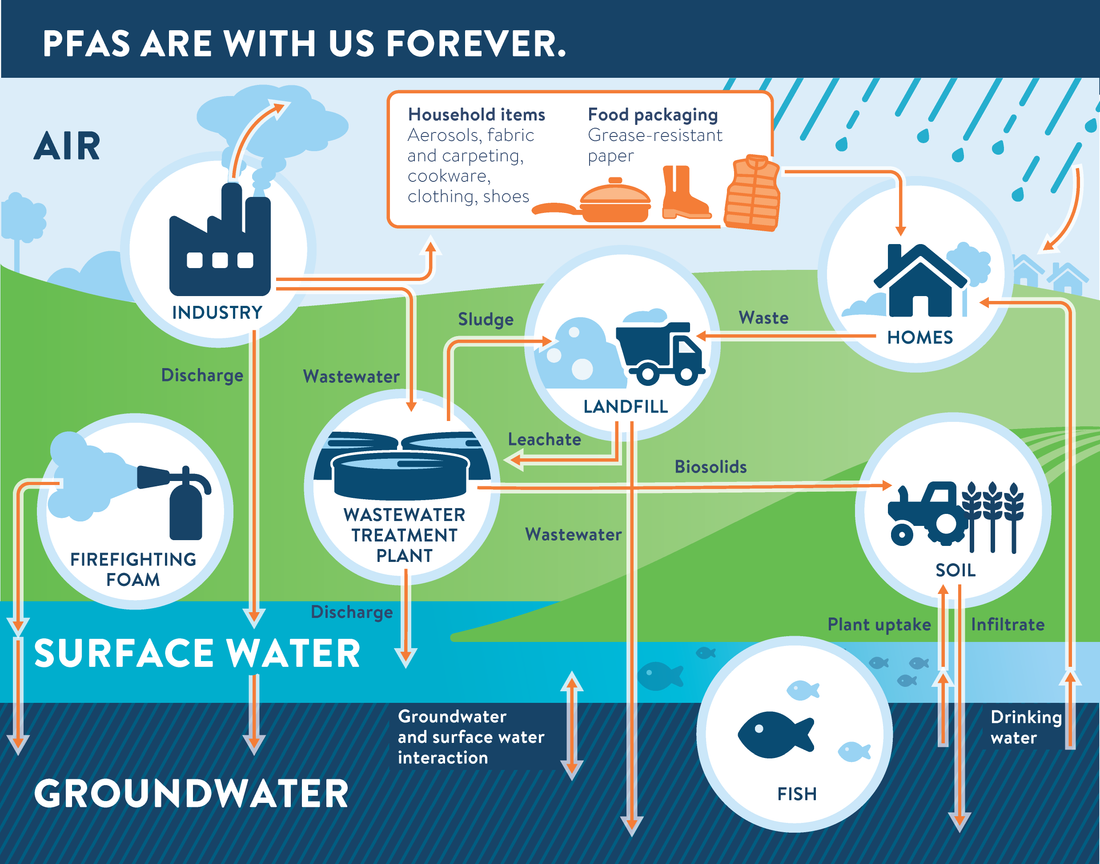
PFAS, or per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, are a group of man-made chemicals used in various consumer products for their water- and stain-resistant properties. These chemicals are extremely stable, meaning they don’t break down naturally, and they can persist in the environment and human body for decades, leading to the nickname “forever chemicals.”
Here’s why PFAS have become a significant health issue:
- Persistent Contamination: Once in the water supply, PFAS spread quickly and are nearly impossible to remove without specialized filtration. Industrial sites, military bases, and landfills are common sources where PFAS enter the water system and travel far from their original source.
- Bioaccumulation: PFAS accumulate in our bodies over time, so even small exposures can build up, leading to higher concentrations that may pose health risks.
- Health Impacts: Research links PFAS exposure to various health problems, including reproductive issues, thyroid disease, weakened immune response, and some types of cancer. Even at low levels, these chemicals can disrupt hormone function and impact child development.
With studies showing that nearly all Americans have detectable levels of PFAS in their blood, concern over these chemicals has grown. Public awareness and regulatory standards are still catching up, but individuals can take proactive measures to reduce their exposure.
How PFAS Make Their Way Into Our Drinking Water
Despite efforts to regulate PFAS in some industries, the chemicals are already widely dispersed in soil, rivers, and groundwater. Here are some common ways PFAS can enter your water supply:
- Industrial Discharge: Manufacturing facilities that produce items like non-stick cookware, firefighting foams, and water-repellent clothing are major sources of PFAS. Waste from these facilities can leach into nearby water sources.
- Runoff and Landfill Leachate: PFAS-containing products discarded in landfills can leach chemicals into the ground over time. Agricultural and industrial runoff also carry PFAS into lakes and rivers that supply water to communities.
- Household Products: Many household items, from carpets to food packaging, contain PFAS. When these items are disposed of or degrade, PFAS can make their way into water sources through wastewater systems.
Because of the persistence of these chemicals, traditional water treatment facilities struggle to filter them out completely. This means that, for many people, PFAS are still present in the water that flows directly into their homes.
Health Risks of PFAS Exposure
The health effects of PFAS exposure are still being studied, but evidence already points to several concerning risks. Some of the potential impacts include:
- Hormone Disruption: PFAS can interfere with the body’s natural hormone systems, particularly affecting thyroid function, which plays a key role in metabolism and energy regulation.
- Immune System Suppression: Studies indicate that PFAS exposure can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and potentially reducing vaccine effectiveness.
- Developmental Delays in Children: Exposure to PFAS has been linked to developmental delays in infants and children, including lower birth weights and delayed growth.
- Increased Cancer Risk: PFAS exposure is associated with an increased risk of certain cancers, particularly kidney and testicular cancer. The chemicals can also impact liver function and cholesterol levels.
With such a wide range of potential health effects, minimizing PFAS exposure is crucial for long-term well-being, especially for children and other vulnerable populations.
Why Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems Are the Solution
Given the resilience of PFAS in water, standard home filters may not be enough to remove them. However, reverse osmosis (RO) systems are among the most effective filtration methods for dealing with PFAS contamination. Here’s how RO systems provide a reliable defense:
- Advanced Filtration Capabilities
Reverse osmosis systems use a semi-permeable membrane that blocks contaminants from passing through, effectively filtering out even microscopic PFAS particles. RO systems typically remove 99% of PFAS, ensuring that only clean, filtered water reaches your taps.
- Multi-Stage Filtration for Added Protection
RO systems often use several stages of filtration, which can include sediment filters, carbon filters, and the RO membrane itself. These multiple stages target not only PFAS but also other potential contaminants like chlorine, lead, and heavy metals, offering a comprehensive water purification solution.
- Peace of Mind with Safe Drinking Water
With an RO system in place, you can feel confident that you and your family are consuming water that’s free of harmful chemicals. Whether it’s for drinking, cooking, or making coffee, RO-filtered water offers peace of mind by reducing your exposure to toxic substances.
- Minimal Maintenance, Maximum Impact
Once installed, RO systems are relatively low-maintenance, typically requiring filter changes every 6-12 months. This makes them a convenient option for households wanting reliable filtration without constant upkeep.
Choosing the Right Reverse Osmosis System for Your Home
When selecting an RO system, it’s essential to choose one with high-quality filters and membranes capable of removing PFAS. Here are a few things to look for:
- Certified PFAS Removal: Check for NSF/ANSI certifications or third-party testing that guarantees effective PFAS filtration.
- Multiple Filtration Stages: Look for systems with at least three stages of filtration, including a sediment pre-filter, activated carbon filter, and RO membrane.
- Capacity and Flow Rate: Choose a system that meets your household’s daily water needs, ensuring a steady flow of filtered water.
Since RO systems can vary widely in quality and capabilities, reading reviews and seeking professional advice can help you find the best solution for your specific water quality concerns.
Final Thoughts
With PFAS contamination in water supplies across the country, taking steps to protect your family from these harmful chemicals is more important than ever. Reverse osmosis systems offer a powerful solution, filtering out PFAS and other contaminants to provide safe, clean drinking water.
While regulatory changes may take years, a home RO system can help you take control of your water quality right now, safeguarding your health for years to come.
